Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a revolutionary force in diverse industries, and nursing and midwifery are no exceptions.
The integration of AI technologies has the potential to reshape healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare systems. But with AI’s potential, there are also certain challenges and concerns that we need to consider.
What exactly is AI? It is the ability of computers to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision making.
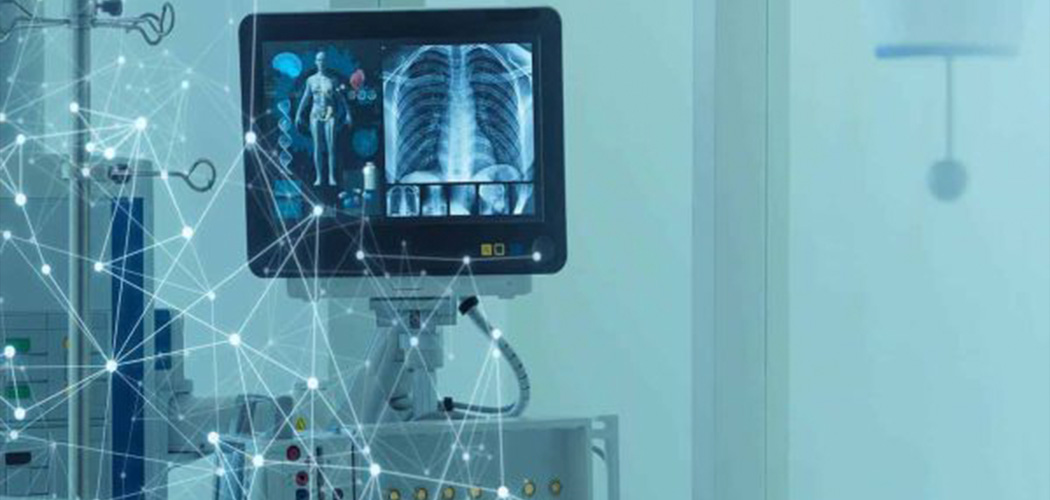
For example, in healthcare, AI can be used to analyse medical imaging scans and X-rays to eliminate the risk of human error.
The media often refers to AI as a website called ChatGPT. This is a natural language processing tool driven by AI technology that can write an essay, compose a song, create a poem or even ‘paint’ in a particular style.
It could fool you into believing a human produced the results. But AI is not sentient – it is a combination of software and hardware that appears to have human-like intelligence and reasoning.
If carefully implemented, AI presents certain unique benefits for our professions, including:
- Relieving the burden of ever-increasing administration needs via automating routine tasks.
- Helping nurses make more accurate and timely diagnoses, potentially leading to better treatment outcomes.
- Analysing large datasets to identify trends and patterns not apparent to clinicians, leading to earlier detection of diseases and improved patient care.
- Streamlining administrative processes and reducing errors in diagnosis and treatment for cost savings in healthcare delivery, which can then be redirected towards better healthcare outcomes.
While integrating AI into nursing holds immense promise, it also presents certain challenges and ethical considerations. Privacy and security of patient data are paramount concerns, as AI relies on vast amounts of sensitive information. There are many examples of AI technologies that, due to poor design, did not perform as expected or promised.
For example, in 2021, a paper published in Nature Machine Intelligence explored the use of AI in diagnosing via medical imaging the COVID-19 virus. The dataset used to train the AI included patients imaged when lying down (eg. CXR CT scans). Those lying down were much more likely to be seriously ill, so the algorithm learned to identify COVID risk based on the person’s position in the scan. Consequently, the AI model was flawed.
AI implementation requires caution and should not replace critical thinking – the core of nursing and midwifery. We must question, analyse, evaluate and judge what we hear or see. Critical thinking in healthcare is most crucial when new information is obtained and a quick decision is needed. AI is only as good as its programming and data that it has access to. Relying on AI and not thinking critically about every patient care decision could be problematic.
AI lacks empathy. This is a human quality. As well as critical thinking, empathy can direct how we provide care. Computers cannot provide nursing and midwifery values such as compassionate and patient-centred care provision and respect for diverse perspectives.
The implementation of AI in healthcare must involve nurses and midwives in its development. We are the largest and most trusted group of healthcare professionals and have direct and frequent contact with patients, parents and families. We have rich, nuanced and diverse knowledge and experience in clinical practice and education. Therefore, nurses and midwives should be involved in conceptualising, designing, testing, and evaluating AI technologies to ensure that they are relevant, useful, and acceptable for our practice and patient care. If AI is introduced with the involvement of our profession, then there is more likely to be a positive attitude towards it.
Importantly, nurses and midwives should also collaborate with other stakeholders, such as patients, researchers, developers, and policymakers, to ensure that AI technologies are ethical, legal, and safe.
Nurses, midwives, and healthcare institutions must approach AI integration thoughtfully, ensuring that ethical and regulatory concerns are addressed. Training and education will be essential to prepare nurses for the AI-augmented healthcare landscape. By embracing AI while preserving the core values of nursing and midwifery, our professions can harness the power of technology to provide even better patient care, ultimately leading to a healthier and more efficient healthcare system.







One Response
The use of AI in psychiatric nursing care brings several benefits, particularly in assisting with the documentation of facts. Here are some key advantages:
1. Efficiency: AI can automate routine tasks involved in documentation, such as data entry and record-keeping. This saves time for psychiatric nurses, allowing them to focus more on direct patient care and critical thinking.
2. Accuracy: AI technologies can help ensure the accuracy of documentation by flagging inconsistencies, errors, or missing information. This reduces the risk of inaccuracies in patient records, which is crucial in psychiatric care where precise and comprehensive documentation is vital.
3. Standardization: AI can assist in maintaining consistent documentation practices within psychiatric care. By providing templates, guidelines, and prompts, AI can help nurses adhere to standardized protocols and ensure that all necessary information is included in the documentation.
4. Data Analysis: AI tools can analyze large datasets of psychiatric patient information to identify patterns and trends. This can assist psychiatric nurses in making more informed decisions and formulating individualized care plans based on data-driven insights.
5. Decision Support: AI can provide decision support to psychiatric nurses by offering evidence-based recommendations and guidelines during the documentation process. This can help nurses ensure that their care plans and interventions align with best practices and research findings.
6. Time-saving: AI can automatically extract relevant information from medical literature, research articles, and clinical guidelines, providing nurses with up-to-date and pertinent information without the need for extensive manual searching. This saves time and enhances the accuracy of information used in psychiatric nursing care.
7. Collaboration and Communication: AI tools can facilitate collaboration and communication among healthcare professionals involved in psychiatric care. By providing a centralized platform for sharing and accessing patient information, AI can improve care coordination and ensure that all team members have access to accurate and timely documentation.
Overall, the use of AI in psychiatric nursing care can streamline documentation processes, enhance accuracy, provide data-driven insights, support decision-making, and foster collaboration. By leveraging AI technologies, psychiatric nurses can devote more time and attention to direct patient care, ultimately improving the quality of care provided to individuals with mental health needs.
PS: This reply is AI assisted – total time taken 3 minutes.